at home
Our house is much more than the place where we live – it is our home, our refuge, where we are protected. The environment that we create in
our home is essential to be comfortable and healthy, the air we breathe in it must be as clean as possible.

Pollution in the home
The pollutants inside our home are more concentrated than outside since, in addition to the pollution that can be filtered from outside there are several sources of pollutants inside the home itself. For example, the inhabitants themselves or even pets.
Tobacco smoke is one of the most prominent pollutants, but you also have to take into account others such as water and humidity, which contribute to the appearance of molds, fungi, allergens and bacteria. Another source of pollution are the materials used in construction and furniture, which emit a series of volatile organic compounds that float in the air and can be harmful to your health. Likewise, the chemicals we use for cleaning, air fresheners, pesticides, paints, etc., are a source of exposure to dangerous particles.
Careless maintenance of the home and its equipment can also lead to contamination. Cracks in the walls, for example, allow the infiltration of radon gas, which also has harmful health effects.1

How to Measure the Quality of the Air You Breathe at Home?
To know the quality of the air in your home, different aspects must be taken into account. First and foremost is the satisfaction of the occupants with respect to the air they are breathing. For this, some of the items that can be taken into account include whether they perceive unpleasant odors or if they have symptoms related to poor quality air.
The concentration of pollutants can also be analyzed by different methods such as direct reading through continuous analysis with specific devices or taking samples to later study.
There are different types of devices for measuring indoor air quality. These continuously monitor the environment and alert when recommended contamination levels have exceeded. In addition, they advise when it is better to ventilate the house based on the quality of the outside air. The technologies used are2:
- CO2 sensors: They measure the concentration of this gas in parts per million (ppm) through infrared.
- VOC concentration sensors: They calculate the amount of volatile organic compounds (VOC) that are present in the air. They can come from a variety of sources, such as cleaning and hygiene or construction products.
- PM2.5 sensors: Suspended fine particles can cause respiratory problems. To measure its presence in the air, laser type sensors are used
- Humidity sensors: Evaluate humidity and temperature to prevent the growth of molds and unwanted bacteria.
Problems derived from poor quality indoor Air
The World Health Organization estimates that exposure to indoor pollution can cause from mild effects on the respiratory tract such as nasal congestion, sneezing, conjunctivitis, etc., to systemic effects such as headache, difficulty concentrating, etc. Among the most serious effects, chronic respiratory diseases, asthma, muscle pain, seizures, endocrine disturbances, and many more have been documented. Ultimately, it has been shown that there is a direct relationship between indoor air pollution and health.3
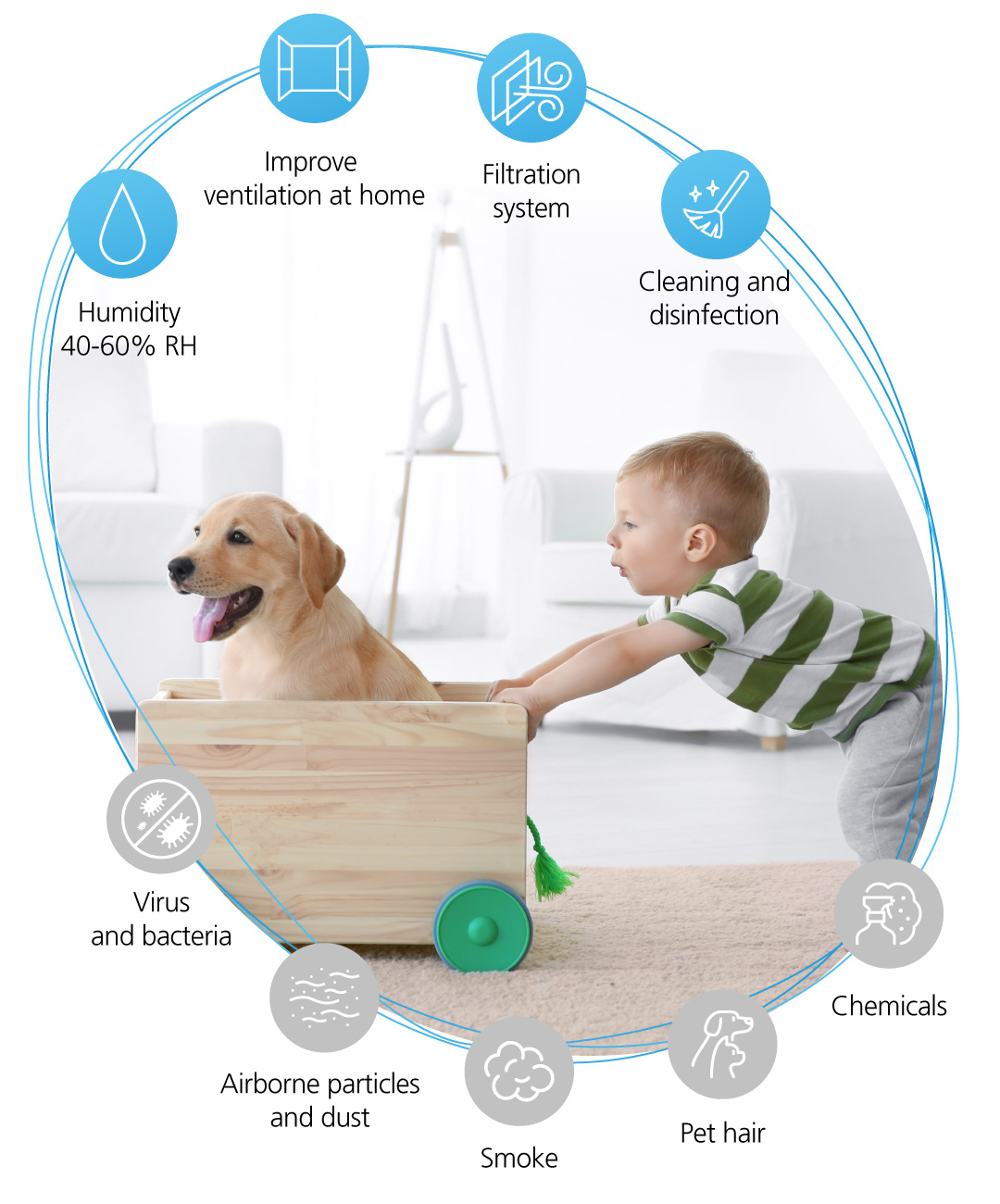
Tips
- Ventilate your home on a daily basis.
- Use filtration and air purification systems.
- Do not smoke indoors.
- Use the extractor hood while cooking.
- NASA4 recommends decorating your home with plants like pothos, bamboo palm, plants or snake plants, which absorb air pollutants.
- Control the indoor humidity level to be around 40%. Watch for possible water leaks on the ceiling or walls and avoid hanging clothes inside.
- Maintain an adequate and comfortable temperature, especially in the rooms that you frequent the most.5
- Make sure that the materials of the furniture, paintings or fabrics are of natural origin.